This has become–by far–the most visited page on Evanna’s site.
So before answering the question of what spina bifida is, let me explain what is it not, because the diagnosis is often hard-hitting, emotional, and followed by information from medical professionals that is often outdated, over-generalized, or just plain inaccurate.
First and foremost: spina bifida is not a death sentence. With advances in treatment and care over the past few decades, over 90% of people with SB live well into adulthood.
SB is what’s known as a ‘snowflake condition‘; that is, it affects each person differently. This is part of the reason that the information you may have been given about prognosis is inaccurate.
SB is not your fault. You’ll most often hear about folic acid, and while that can sometimes be one of the components, there are also genetic and environmental elements at play as well.
What then is spina bifida?

Spina bifida is a type of birth defect called a neural tube defect. It occurs at the point when the neural tube (which forms the spinal column and spinal cord) doesn’t fully close.
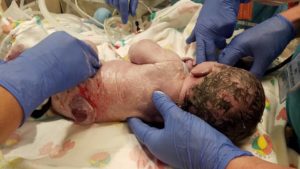
Evanna’s is the most rare and severe form, myelomeningocele, where part of the spinal nerves push out of the spinal canal, and the nerves are often damaged.
Evanna’s:
More details below from The Spina Bifida Association:
What is Spina Bifida?
Spina Bifida is the most common permanently disabling birth defect in the United States.
What is Spina Bifida?
Spina Bifida literally means “split spine.” Spina Bifida happens when a baby is in the womb and the spinal column does not close all of the way. Every day, about eight babies born in the United States have Spina Bifida or a similar birth defect of the brain and spine.
What causes Spina Bifida?
No one knows for sure. Scientists believe that genetic and environmental factors act together to cause the condition.
What are the different types of Spina Bifida?
Occult Spinal Dysraphism (OSD)
Infants with this have a dimple in their lower back. Because most babies with dimples do not have OSD, a doctor has to check using special tools and tests to be sure. Other signs are red marks, hyperpigmented patches on the back, tufts of hair or small lumps. In OSD, the spinal cord may not grow the right way and can cause serious problems as a child grows up. Infants who might have OSD should be seen by a doctor, who will recommend tests.
Spina Bifida Occulta
It is often called “hidden Spina Bifida” because about 15 percent of healthy people have it and do not know it. Spina Bifida Occulta usually does not cause harm, and has no visible signs. The spinal cord and nerves are usually fine. People find out they have it after having an X-ray of their back. It is considered an incidental finding because the X-Ray is normally done for other reasons. However, in a small group of people with SBO, pain and neurological symptoms may occur. Tethered cord can be an insidious complication that requires investigation by a neurosurgeon.
Meningocele
A meningocele causes part of the spinal cord to come through the spine like a sac that is pushed out. Nerve fluid is in the sac, and there is usually no nerve damage. Individuals with this condition may have minor disabilities.
Myelomeningocele (Meningomyelocele), also called Spina Bifida Cystica
This is the most severe form of Spina Bifida. It happens when parts of the spinal cord and nerves come through the open part of the spine. It causes nerve damage and other disabilities. Seventy to ninety percent of children with this condition also have too much fluid on their brains. This happens because fluid that protects the brain and spinal cord is unable to drain like it should. The fluid builds up, causing pressure and swelling. Without treatment, a person’s head grows too big, and may have brain damage. Children who do not have Spina Bifida can also have this problem, so parents need to check with a doctor.
How is Spina Bifida Treated?
A child with Meningomyelocele usually is operated on within two to three days of birth. This prevents infections and helps save the spinal cord from more damage.
A child with Meningocele usually has it treated with surgery, and more often than not, the child is not paralyzed. Most children with this condition grow up fine, but they should be checked by a doctor because they could have other serious problems, too.
A child with OSD should see a surgeon. Most experts think that surgery is needed early to keep nerves and the brain from becoming more damaged as the child grows.
Spina Bifida Occulta usually does not need to be treated. ‘
What can you do to prevent Spina Bifida?
Women who are old enough to have babies should take folic acid before and during the first three months of pregnancy. Because half of the pregnancies in the United States are unplanned, the Spina Bifida Association asks women to take a vitamin with 400 mcg (0.4 mg) of folic acid each day during the years of their lives when they are possibly able to have children.
Women who have a child or sibling with Spina Bifida, have had an affected pregnancy or have Spina Bifida themselves should take 4000 mcg (4.0 mg) of folic acid for one to three months before and during the first three months of pregnancy.
Learn more about this disease and how you can help patients by visiting The Spina Bifida Association.
